Used typically with heavy duty applications such as CNC machining equipment, automated assembly machinery, tooling and cutting, machine slides are able to handle massive loads. These motorized linear slides offer precision movement capabilities along vertical or horizontal rails that can be single, double or multi-axis. Read More…
Del-Tron is a linear slide manufacturer/distributor of ball bearing slides, crossed roller tables, roller slides, multi-axis positioning stages, xy tables, motor-ready lead screw stages & crossed roller rail sets.

When describing Tusk Direct, a linear slide distributor, products such as linear motion components, roller tables, ball & crossed roller slides, dovetail slides, bushings, multi-axis positioners & motor ready lead screw actuators, come to mind.

Isotech is a distributor of precision linear motion components: air cylinders, linear actuators, linear slides, ball slide assemblies, crossed roller slide assemblies, re-circulating ball slide guides. We can supply standard or high precision products in either English or metric, all with the convenience of on-line ordering. Our parts are ready for installation right out of the box.

Established in 1967, Velmex makes manual & motor driven dovetail slides, open frame tables, twin rail slides, rotary and XY stages. Choose hand, lead screw or belt drive.

More Machine Slide Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Machine Slides: Design, Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
Machine slides are critical components in modern automated machinery and precision engineering. They enable linear motion and accurate positioning in a wide range of industrial and manufacturing settings. Understanding the mechanics, types, materials, and selection factors for machine slides is essential for engineers, maintenance professionals, and procurement specialists seeking to optimize machine performance, longevity, and precision.
How Do Machine Slides Operate?
Machine slides are moved by drive mechanisms; these mechanisms can be mechanical, hydraulic, or electronic. Each drive method provides unique advantages based on application needs and performance requirements.
- Mechanical drive mechanisms (such as ball screws or lead screws) offer high accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for CNC machinery, robotics, and laboratory automation.
- Hydraulic slide drives deliver significant force and are often chosen for heavy-duty manufacturing, metalworking, and stamping operations where high load capacity is necessary.
- Electronic (servo or stepper motor-driven) slides provide rapid, programmable precision for automated assembly lines, semiconductor manufacturing, and packaging systems.
Machine slides are designed to have close tolerances and high rigidity to ensure that motion, even in high-paced applications, is controlled. This reliability is vital for maintaining process quality, reducing downtime, and achieving tight manufacturing tolerances.
Machine Slide Construction: Key Components and Materials
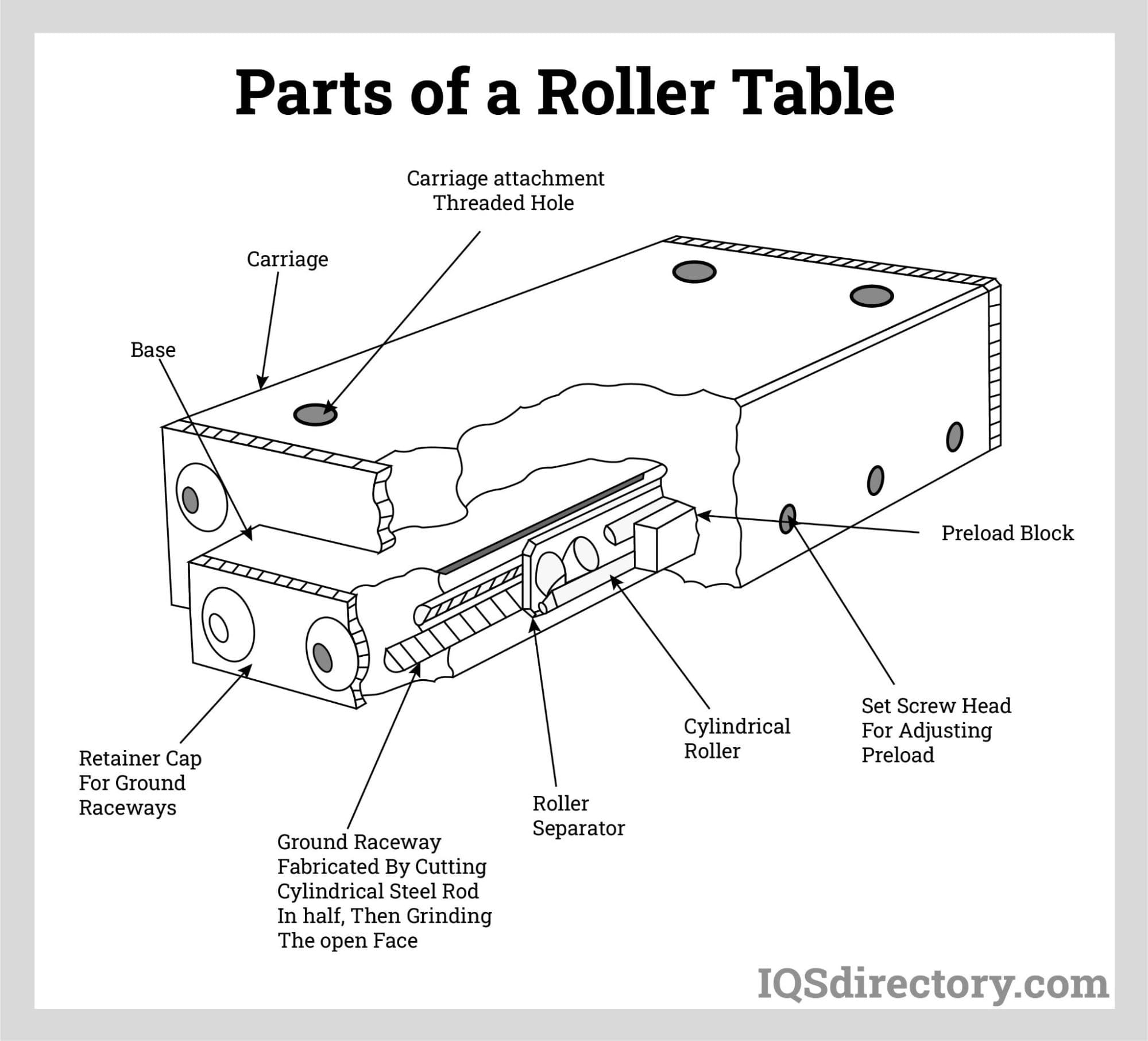
The slides consist of a stationary base which holds the linear rails and a moving component, or carriage, that is attached to the bearings channels and moves along the cylindrical or ball bearing slides within the railings.
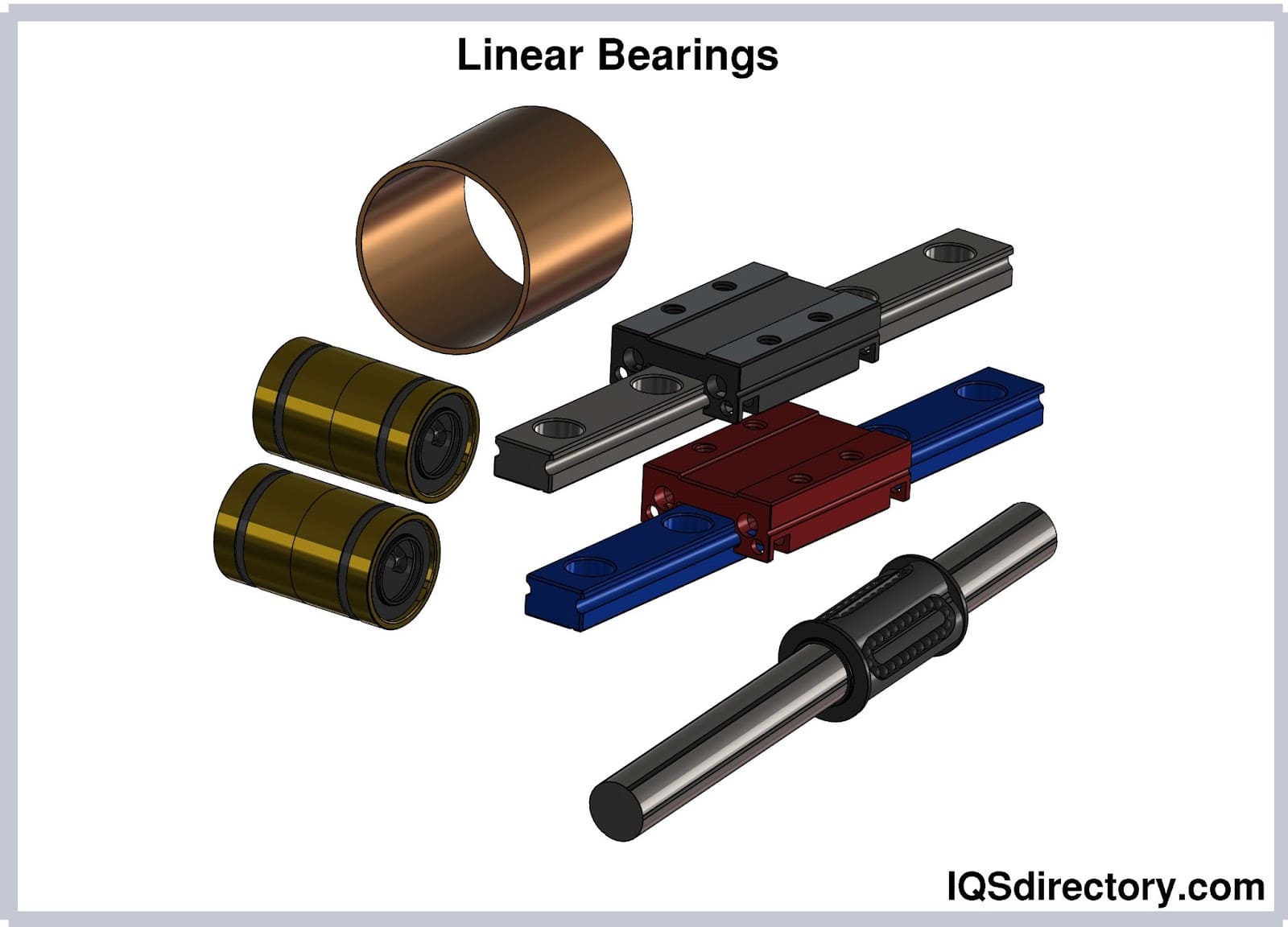
High-quality machine slides use advanced bearing systems—such as recirculating ball bearings, roller bearings, or plain bearings—to minimize friction and enable smooth, precise motion. The stationary base provides structural support and alignment for the moving carriage, which is engineered to carry loads with minimal deflection.
Common Materials for Machine Slides
- Stainless steel: Known for corrosion resistance and strength, stainless steel slides are preferred for food processing equipment, medical devices, and environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
- Cast iron: Highly durable and capable of maintaining structural integrity under heavy loads. Cast iron slides are common in traditional industrial machinery.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to oxidation, aluminum slides are suitable for applications where weight reduction and moderate load capacity are priorities, such as electronics assembly and light automation.
Material choice is dependent upon the specifics of the application and the intended work environment and load capacity. For buyers, understanding the operational environment—such as exposure to corrosive agents, extreme temperatures, or abrasive contaminants—guides optimal material selection to maximize service life and minimize maintenance.
Types of Machine Slides: Exploring Motion Solutions
There are several distinct types of machine slides, each engineered to suit particular industrial applications. The primary types include:
- Dovetail slides: These slides are often used in machine slide processes because of their increased precision and close tolerance performances. The dovetail shape offers excellent rigidity and resistance to side loading. The slides also have a gib, which ensures the components stay in place along the linear rails and compensates for any slip-stick motion that may inadvertently occur. Dovetail slides are common in toolmaking, optical equipment, and manual adjustment stages.
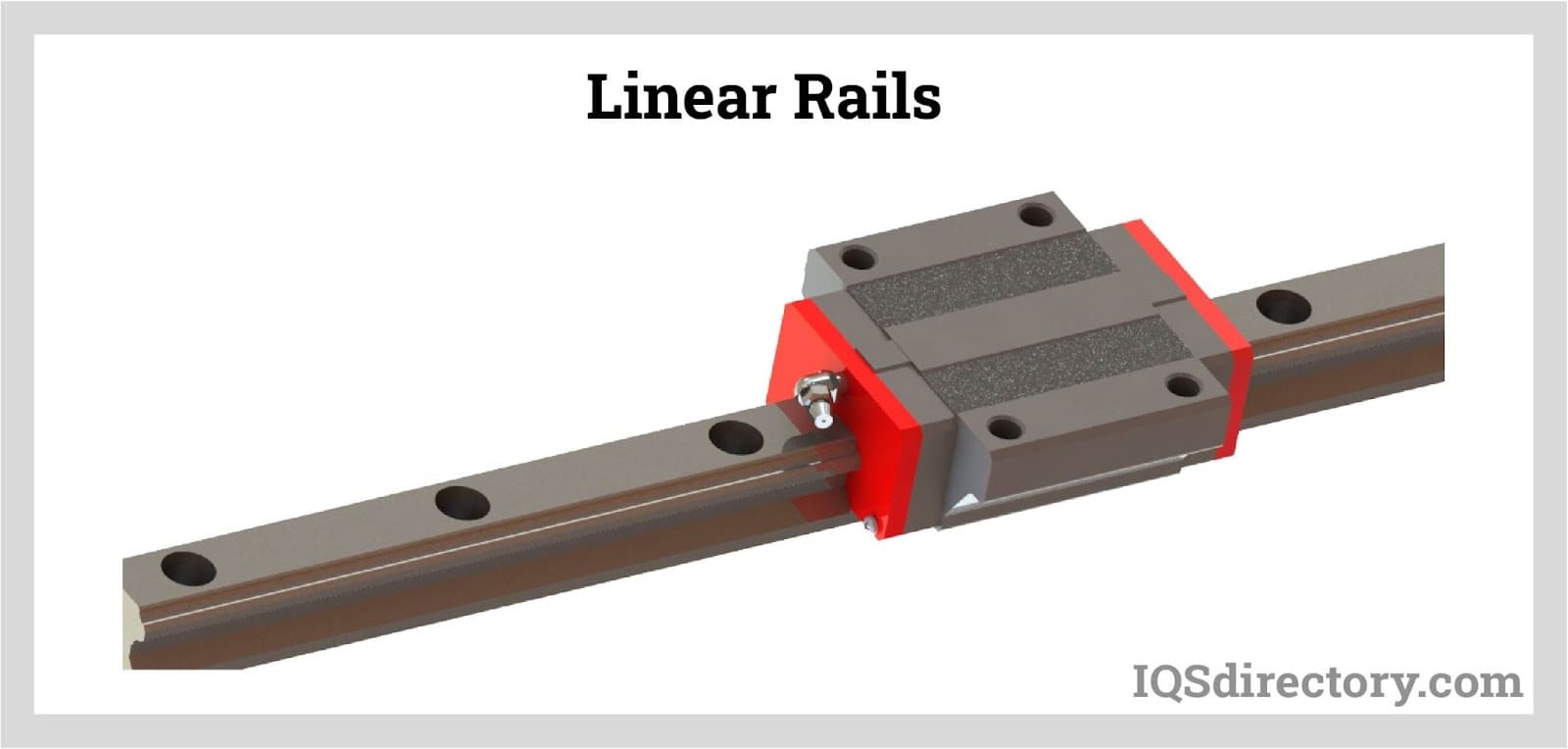
- Ball bearing slides: Utilizing recirculating ball bearings, these slides operate with exceptionally low friction and are ideal for high-speed, repetitive motion applications in electronics manufacturing, laboratory automation, and precision assembly.
- Roller slides: These use cylindrical rollers instead of balls, providing greater load capacity and smoother movement under heavy loads. Roller slides are often chosen for machine tools, press brakes, and heavy-duty automation systems.
- Four-slide machines: A specialized type of machine slide used to manufacture metal parts by using moving mechanisms on four separate axes that act upon the metal to create a finished component. They are able to produce completed components in fast turnaround times, making them indispensable in high-volume metal stamping and forming.
- Crossed roller slides: Featuring alternating rollers oriented at right angles, these slides deliver precise, smooth travel and are favored in metrology, medical imaging, and semiconductor processing equipment.
- Air bearing slides: These employ a thin film of pressurized air to support the load, eliminating mechanical contact and offering virtually frictionless movement. Air bearing slides are used in ultra-high-precision applications, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and wafer inspection systems.
Not sure which type of machine slide is right for your application? Ask yourself: What level of precision and rigidity is required? Will the slide be exposed to harsh environments or contaminants? How important are speed and cycle times? Evaluating these questions can dramatically narrow your options and help you select the optimal motion solution.
Machine Slide Drive Options: Motion Control Technologies
To achieve controlled and repeatable motion, machine slides can be actuated by several different drive technologies. Understanding these drive mechanisms is essential for engineers and machine designers seeking to match performance with operational requirements.
Common Drive Mechanisms
- Ball screw drives: Offer high positional accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency. Ball screw-driven slides are used extensively in CNC machinery, pick-and-place systems, and other high-precision automation equipment. Searching for ball screw slide performance data? Compare load ratings and backlash specifications to ensure optimal fit.
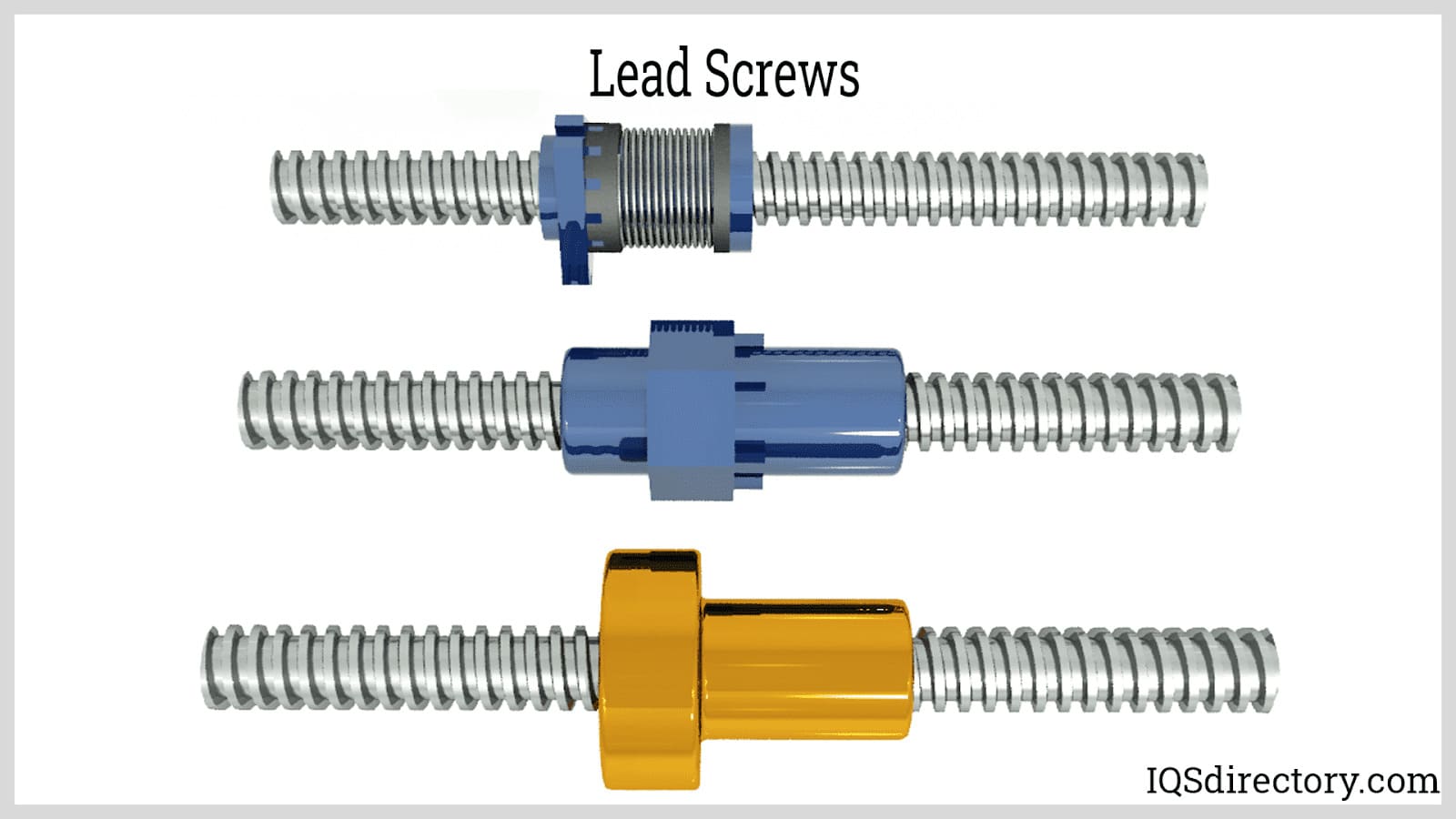
- Lead screw drives: Simpler and more cost-effective than ball screws, lead screw slides provide reliable movement for moderate-precision applications, such as laboratory jigs and manual positioning stages.
- Air or hydraulic cylinders: Deliver strong, linear force for actuation. Pneumatic slides are valued for speed and clean operation, while hydraulic slides offer high force for heavy industrial tasks. Evaluate force requirements and available infrastructure when choosing between air and hydraulic actuation.
- Rack and pinion drives: Suitable for long travel distances and high speeds, rack and pinion slides are ideal for material handling, gantry systems, and large-scale assembly equipment.
- Linear motor drives: Provide direct, non-contact motion for applications requiring ultra-fast, vibration-free movement, such as semiconductor wafer handling and laser machining.
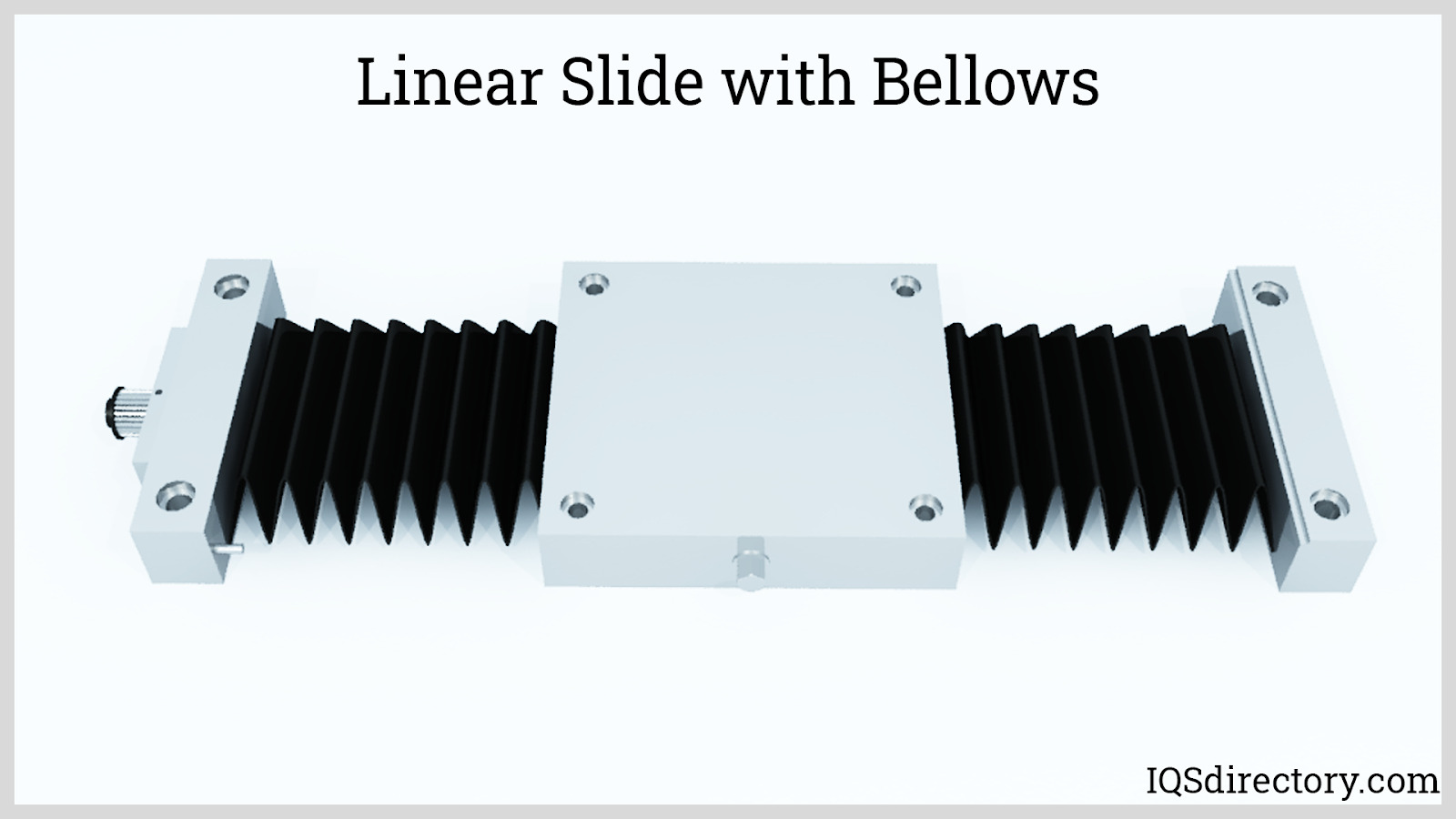
Also, machine way wipers are used with machine slides to protect the equipment against wear and tear from dust and debris along the linear rails. The wipers move in front of the carriage or sliding mechanism to ensure smooth movement of the bearings and rail. Covers, bellows, or other linear rail shields can also be used to further protect against the contamination of the bearing system within the linear system.
Key Benefits of Implementing High-Quality Machine Slides
Investing in high-performance machine slides delivers significant advantages in industrial automation, manufacturing, and precision engineering environments. These benefits include:
- Enhanced accuracy and repeatability: Achieve tighter tolerances and consistent positioning for improved product quality and process reliability.
- Increased machine uptime: Durable materials and reliable drive mechanisms reduce maintenance intervals and minimize unexpected downtime.
- Optimized workflow efficiency: Fast, smooth, and controlled linear motion leads to higher throughput, reduced cycle times, and scalable production capabilities.
- Extended equipment life: Protective features—such as way wipers, rail covers, and robust construction—safeguard slides from environmental hazards, enhancing operational longevity.
- Customizability: Many machine slides can be tailored to fit specific application needs, including travel length, load rating, mounting options, and environmental protection requirements.
Applications of Machine Slides: Where Precision Meets Productivity
Machine slides are indispensable in a wide variety of industries and processes, including:
- Automated manufacturing systems: For precise component transport, assembly, and inspection in automotive, electronics, and consumer goods production lines.
- Metalworking and machining centers: Used in CNC mills, lathes, and grinders for tool positioning, part loading, and workpiece manipulation.
- Laboratory and medical equipment: For sample positioning, microscope stages, and medical device automation requiring micron-level accuracy.
- Packaging and material handling: Machine slides facilitate rapid product movement, sorting, and packaging in food and pharmaceutical processing plants.
- Optics and photonics: Vital for alignment and adjustment in laser systems, imaging devices, and optical bench applications.
- Robotics: Enabling precise linear motion in robotic arms, pick-and-place units, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
- Semiconductor fabrication: Supporting ultra-clean, vibration-free positioning in wafer handling, inspection, and lithography systems.
- Metrology and inspection: Providing stable, accurate movement in coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and test instrumentation.
Curious how machine slides can improve your specific process? Contact our experts or request a quote to discuss custom solutions for your application.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Machine Slides
Choosing the right machine slide is crucial for system performance and long-term reliability. Consider these essential criteria during the selection process:
- Load capacity: Assess the maximum static and dynamic loads the slide must handle, including any potential shock or vibration.
- Travel distance: Ensure the slide’s stroke length meets your application’s range of motion requirements.
- Precision and backlash: Determine the required positional accuracy and allowable backlash for optimal process results.
- Speed and acceleration: Evaluate the slide’s ability to reach desired speeds without sacrificing stability or service life.
- Mounting and integration: Consider compatibility with existing machine frames, control systems, and ancillary components.
- Environmental considerations: Factor in exposure to dust, moisture, chemicals, or temperature extremes, and specify appropriate protective features.
- Maintenance and serviceability: Opt for slides with accessible lubrication points, replaceable wipers, and easy-to-service designs to minimize downtime.
- Budget and total cost of ownership: Balance initial investment with long-term performance, maintenance needs, and potential productivity gains.
Still evaluating your options? Try searching:
- What is the best machine slide for high-speed automation?
- How to choose between dovetail and ball bearing slides?
- What are the maintenance requirements for linear rails?
- How do environmental factors affect machine slide lifespan?
- Where to buy custom machine slides for unique applications?
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management for Machine Slides
Proper maintenance is vital to maximize the performance and lifespan of machine slides. Routine care reduces downtime, preserves accuracy, and protects your investment in high-precision motion control components.
Maintenance Best Practices
- Regular inspection: Check for signs of wear, contamination, or misalignment. Early detection of issues prevents costly breakdowns.
- Lubrication: Maintain appropriate lubrication schedules for bearings and sliding surfaces, using manufacturer-recommended lubricants.
- Wiper and cover replacement: Replace worn way wipers, bellows, or covers to ensure continued protection against debris and contaminants.
- Alignment checks: Verify slide alignment periodically to maintain optimal motion accuracy and reduce uneven wear.
- Performance testing: Monitor slide travel, speed, and repeatability to detect performance drift over time.
Considering an upgrade or retrofit? Upgrading to advanced machine slides with enhanced materials, integrated sensors, or improved drive mechanisms can boost productivity, reduce maintenance, and future-proof your automation systems.
Frequently Asked Questions About Machine Slides
- What is the difference between a linear slide and a machine slide? While the terms are often used interchangeably, a “machine slide” typically refers to a heavier-duty, application-specific component, whereas “linear slides” may include lighter-duty or modular products used in automation and laboratory settings.
- How do I determine the right slide for my application? Consider load requirements, travel distance, precision, speed, and environmental conditions. Consulting with a motion control specialist or manufacturer can help you make an informed decision.
- Can machine slides be customized? Yes. Most reputable manufacturers offer custom machine slides tailored to unique application needs, including special materials, mounting configurations, and protective features.
- What is the typical lifespan of a machine slide? With proper maintenance, high-quality machine slides can last for many years—even in demanding environments. Lifespan is influenced by usage, load, environment, and maintenance practices.
- Where can I source replacement components or order new machine slides? Trusted suppliers and manufacturers specializing in motion control, linear motion systems, and automation components can provide both standard and custom solutions. Contact us for recommendations or to request a quote.
Why Source Machine Slides from Trusted Specialists?
Partnering with an experienced supplier for your machine slide needs ensures you receive:
- Expert engineering support: Comprehensive technical guidance for selecting, integrating, and maintaining machine slides.
- High-quality products: Access to precision-engineered slides built for industrial durability and performance.
- Customization options: Solutions designed around your application’s unique requirements, from materials and coatings to drive mechanisms and mounting.
- Comprehensive after-sales service: Ongoing maintenance, repair, and technical support to maximize your investment.
Ready to improve your automation, manufacturing, or precision engineering systems? Contact us to discuss your needs, request technical data sheets, or receive a tailored quote on premium machine slides and linear motion solutions.
In Summary: Maximizing Value from Machine Slides in Industrial Applications
Machine slides are foundational to precision motion control in countless industries, from advanced manufacturing to scientific research. Selecting the right slide—whether a dovetail slide, ball bearing slide, or a custom-engineered linear system—can dramatically impact productivity, quality, and operational efficiency.
By understanding machine slide types, drive mechanisms, materials, and maintenance best practices, decision-makers can make informed choices that deliver measurable improvements in speed, accuracy, and equipment lifespan. Whether you are retrofitting an existing line, automating a new process, or designing cutting-edge equipment, investing in the right machine slide technology is key to your success.
For more information, visit our resources on linear rails or dovetail slides, or contact our motion control specialists for personalized recommendations and expert support.







 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services