When circular motion is not needed, linear guide rails are one of the best options since they may be utilized to support big loads and make it easier to move things in one linear direction. In addition, they can support an object’s entire weight to make it easier for an actuating component to move it, or they can support one end of the object. In contrast, the other is supported by the actuating component. Read More…
Del-Tron is a linear slide manufacturer/distributor of ball bearing slides, crossed roller tables, roller slides, multi-axis positioning stages, xy tables, motor-ready lead screw stages & crossed roller rail sets.

When describing Tusk Direct, a linear slide distributor, products such as linear motion components, roller tables, ball & crossed roller slides, dovetail slides, bushings, multi-axis positioners & motor ready lead screw actuators, come to mind.

Isotech is a distributor of precision linear motion components: air cylinders, linear actuators, linear slides, ball slide assemblies, crossed roller slide assemblies, re-circulating ball slide guides. We can supply standard or high precision products in either English or metric, all with the convenience of on-line ordering. Our parts are ready for installation right out of the box.

Established in 1967, Velmex makes manual & motor driven dovetail slides, open frame tables, twin rail slides, rotary and XY stages. Choose hand, lead screw or belt drive.

More Linear Guide Rail Manufacturers

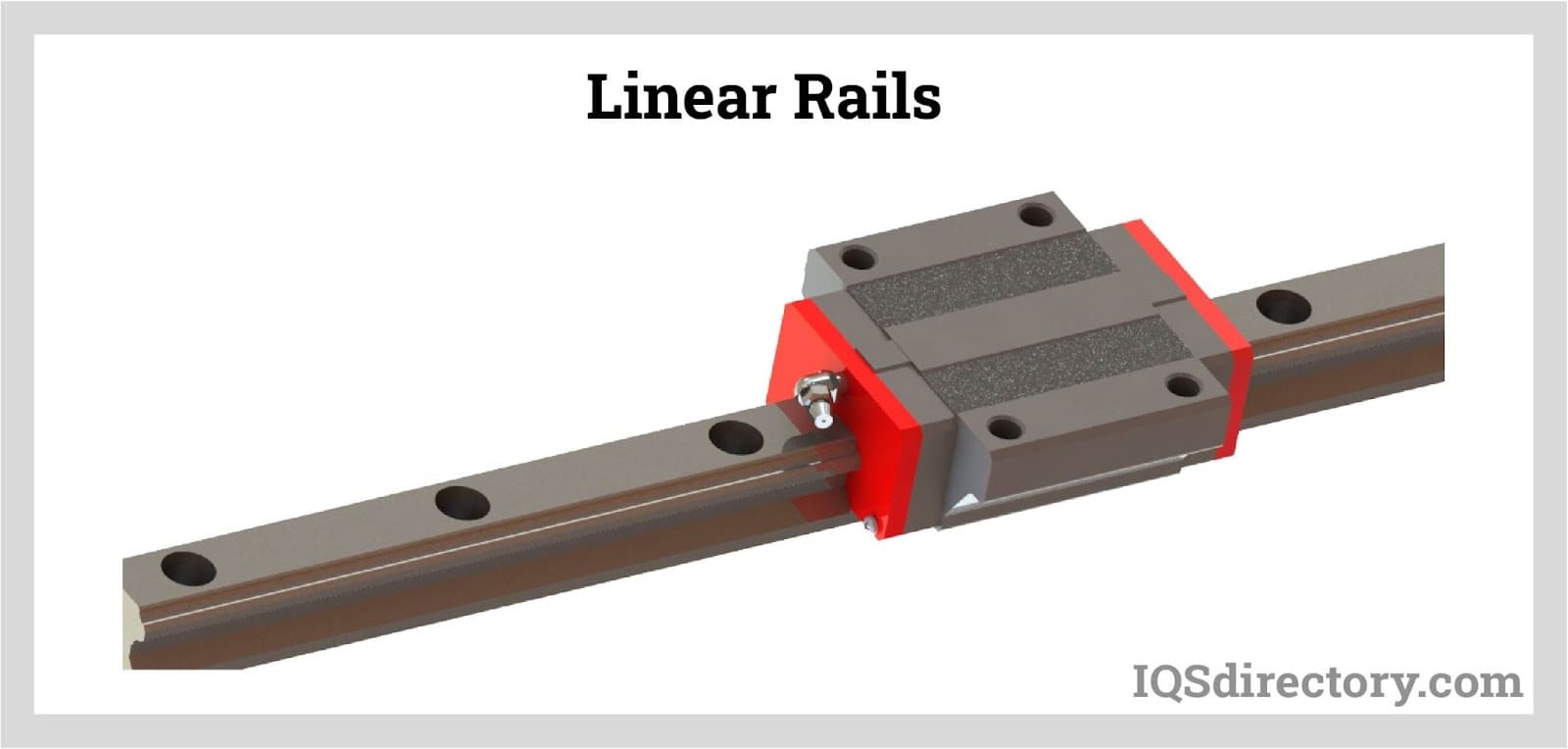
Linear Guide Rail Construction
High-strength, hardened, and galvanized steel is typically used to make linear guide rails to withstand corrosion. The metal is formed and contoured during the cold drawing process before a roller runner is added. Profiled rail guides are typically the best choice for large loads since they are made to offer a very precise linear motion.
There are many different sizes of rail guides, from tiny linear guide rails for cramming tiny components into tight locations to enormous examples for moving components that could weigh more than a ton. To improve the design and safeguard actuating devices, technicians and other users can utilize linear guide rails if they are concerned about side loading in their design.

Applications of Linear Guide Rails
Due to the precise machining of one or both rail edges, which act as reference surfaces, linear guide rails offer high travel accuracy. Together, these features produce a linear guide system perfect for applications needing great precision, rigidity, and long-lasting performance.
Printers and CNC Machines
In CNC machines and 3D printers, both smaller home and bigger industrial printers, linear guides of all shapes and sizes are frequently employed. For example, a tool or base plate is frequently positioned inside a machine using linear guide rails. The linear guide supports the tool's weight or base plate and shields the actuating component from improper loading while another component handles the actuating.

Gantry Robots
In robotic applications and designs, such as the gantry, sometimes known as cartesian robots, and with overhead transport systems, linear guide rails are also used. Individual axes typically have a single linear guide rail and are driven by a screw, belt, and pulley system. Even though there is only one linear rail per axis, very high moment capacities are possible. The use of linear guides to support large loads and provide smooth linear motion is widespread.
Linear Actuators
Linear guide rails are widely employed as the guiding mechanism for actuators driven by belts, screws, or pneumatic cylinders because of their capacity to withstand moment loads. Additionally, they can manage travel speeds of up to 5 m/sec, which is essential in pneumatic and belt systems.
Applications for Single Rails
Linear guide rails may support overhung loads even when only one rail is used because they have load-supporting balls (or rollers) on either side of the rail. Because of this versatility, a single linear rail is used in many applications to save space or prevent misalignment issues with other system components.
Applications for Dual Rails
To convert significant moment loads into forces acting on the bearing blocks, linear rails can be used in pairs. In this architecture, the drive system can be positioned between the linear rails, greatly increasing the system's overall compactness.
Linear Stages
Since stages are very precise systems, travel precision and little deflection are essential. Even when the load is centered on the stage with little to no moment loading, dual linear rails are routinely used to guarantee that stiffness and bearing life are maximized.
Benefits of Linear Rails
- With a little practice, anyone can do the high-quality assembly in no time. Assembly is simple and quick. The transmission mechanism's precision is decided because the machine tool's accuracy is very high. The most frequent parts of the transmission mechanism are a screw and a wire rail. In other words, the accuracy of the wire rail and the screw itself determines the accuracy of the machine. All of them are accessible as common parts. There should be no significant problems as long as the manufacturer's recommendations are followed.
- Several varieties are available based on the rail's structural design, precision level, lubrication strategy, weight-carrying capacity, processing strategy, running speed, and other elements. Depending on the precise parameters of the design, machines can be placed wherever the user pleases.
- The runner moves quickly. Many machine tools operate at incredibly fast speeds, especially when idle. The machine tool is guarded by the rolling friction operation mode and high-precision processing, which is substantial to the credit of the linear rail. The accuracy and stability of high-speed operation have greatly increased processing efficiency and precision.
- Incredibly precise machining is used to construct linear guide rails. As a standard product, the material and the production process of a linear rail have reached a safe, controlled range. As a result, most precision machining machine tools use high-precision linear guides. As a machine tool guide, this also significantly ensures the machine tool's machining accuracy.
Choosing the Proper Linear Guide Rail Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most beneficial outcome when purchasing linear guide rails from a linear guide rail manufacturer, it is important to compare at least five manufacturers using our list of linear guide rail companies. Each linear guide rail manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each linear guide rail business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple linear guide rail companies with the same quote.






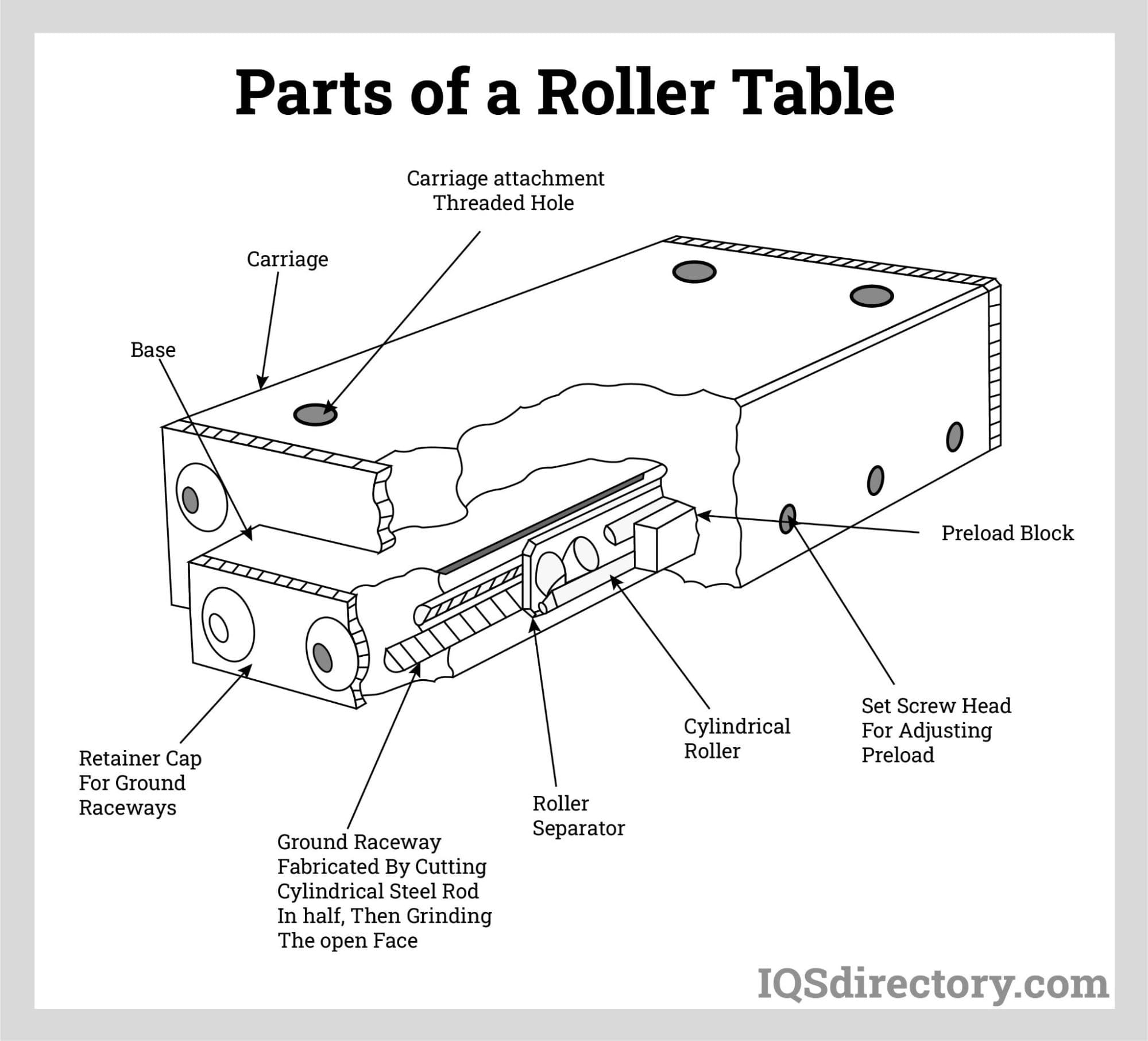

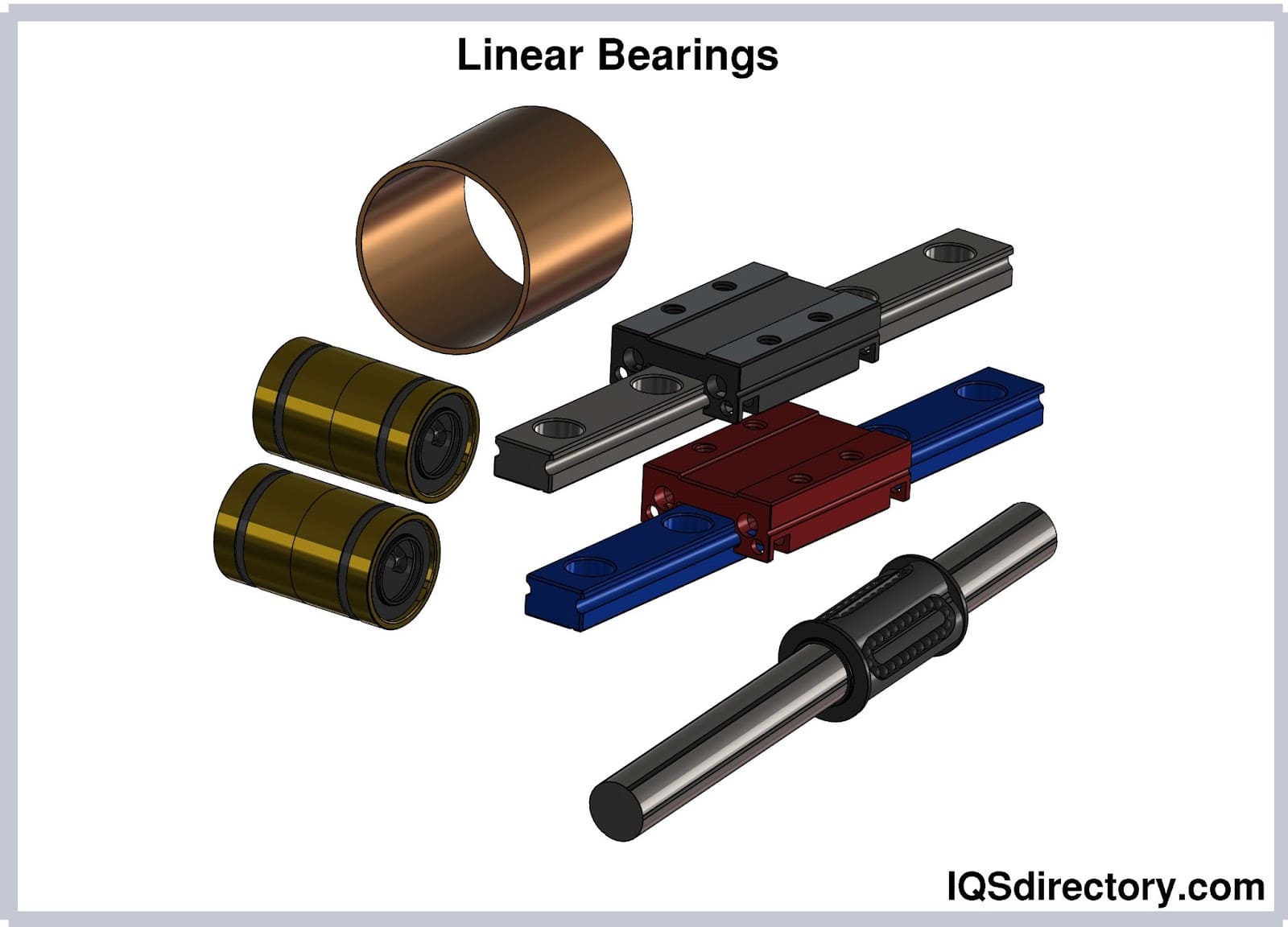
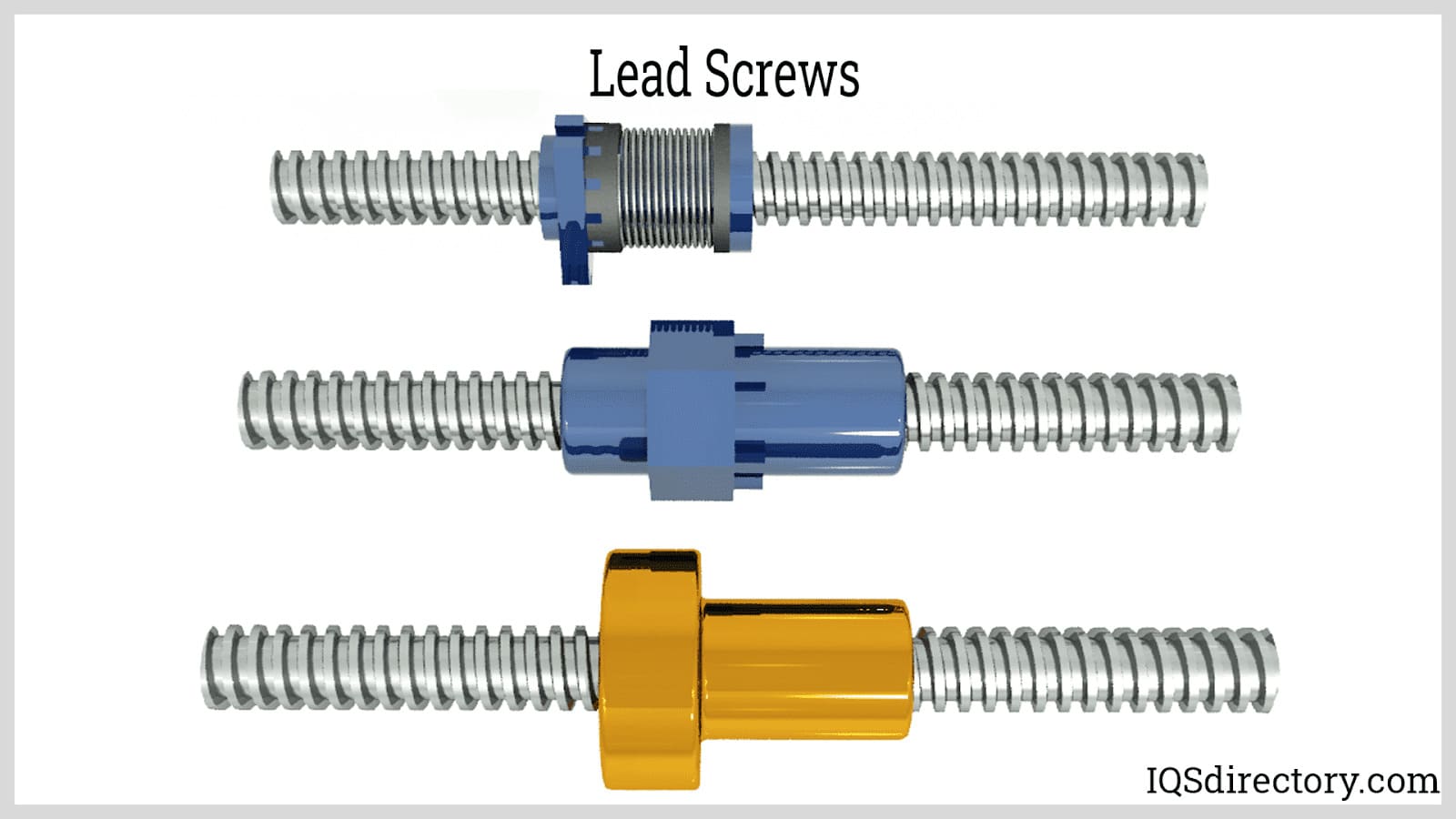
 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services